
The presence of T SCM might be essential for the control of persisting infections, in which effector T cells undergo exhaustion and need to be restored this was supported by the evidence of a negative correlation between the severity of chronic viral ( HIV-1) and parasitic ( trypanosome) infections and the frequency of circulated T SCM cells. Pathogen-specific T SCM cells have been identified in a number of studies of human acute and chronic infections caused by viruses, bacteria and parasites. It also revealed that in type I diabetes patients there was an enrichment of self-reactive clonotypes in T SCM rather than in Tm, suggesting that T SCM might serve as a pool of autoreactive T cells. Īnalysis of TCR β repertoire of T SCM and Tm revealed that T SCM have higher TCRβ diversity compared with Tm, that TCR sequences of T SCM were antigen-experienced and their composition differed with those of naïve T cells. Complex analysis of T SCM dynamics under physiological conditions including stable isotope labeling, mathematical modeling, cross-sectional data from vaccinated individuals, and telomere length analysis revealed that there are at least 2 distinct T SCM subpopulations with different longevity and turnover rates: 1) short-lived, with an average half-life of 5 months, 2) long-lived, with a high degree of self-renewal and the half-life of approximately 9 years, which is consistent with the long-term maintenance of the recall response to antigen (8–15 years).

In another longitudinal study on leukaemia patients who had undergone HSCT, it was reported that genetically modified T SCM could be detected up to 14 years after infusion. Long-term studies on T cells in a cohort of patients vaccinated against yellow fever revealed that vaccine-induced CD8+ T SCM cells specific to yellow fever antigens were stably maintained for 25 years, capable of self-renewal ex vivo, and preserved surface markers and mRNA profiles closest to naïve T cells. Current observations allow to suggest that T SCM is a population which plays an essential role in maintaining a long-term memory in vivo. Multiparametric flow cytometry and TCR sequencing studies showed that more than 30% of naïve T cells primed by antigen directly differentiate into T SCM cells. Īfter primary antigen exposure and elimination, antigen-specific T SCM preferentially survive among memory T cells and stably persist for a long term throughout the human lifespan. Together with the transcriptome analysis of differentially expressed genes reflecting the relatedness of T SCM and Tn cells, these data support the existing hierarchical model of human T cell differentiation: naïve T cells (Tn) → stem cell like memory T cells (T scm) → central memory T cells (Tcm) → effector memory T cells (Tem) / effector T cells (Teff). Longitudinal studies on T SCM dynamics in patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) have shown that donor-derived T SCM cells were highly enriched early after HSCT, differentiated directly from Tn, and that Tn and T SCM cells (but not central memory or effector T cells) were able to reconstitute the entire heterogeneity of memory T cell subsets including T SCM cells. Similarly to memory T cells, T SCM are able to rapidly proliferate and secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines ( IFN-γ, IL-2, and TNF-α) in response to antigen re-exposure, but show higher proliferation potential compared with Tcm cells their homeostatic turnover is also dependent on IL-7 and IL-15. Like naïve T cells, T SCM cells are found more abundantly in lymph nodes than in the spleen or bone marrow but in contrast to naïve T cells, T SCM cells are clonally expanded. These cells represent a small fraction of circulating T cells, approximately 2-3%. T SCM represent an intermediate subset between naïve (Tn) and central memory (Tcm) T cells, expressing both naïve T cells markers, such as CD45RA+, CD45RO-, high levels of CD27, CD28, IL-7Rα (CD127), CD62L, and C-C chemokine receptor 7 ( CCR7), as well as markers of memory T cells, such as CD95, CD122 (IL-2Rβ), CXCR3, LFA-1.
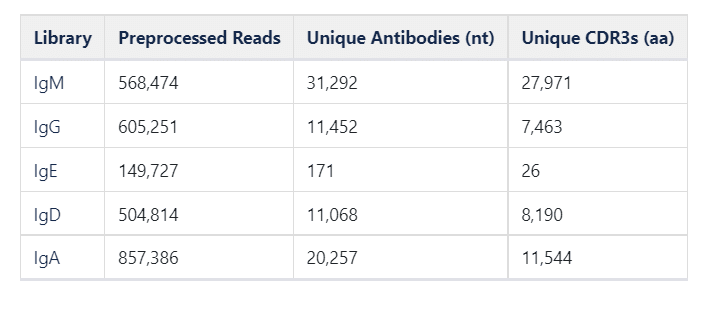
Immune repertoire sequencing challanges full#
A T memory stem cell (T SCM) is a type of long-lived memory T cell with the ability to reconstitute the full diversity of memory and effector T cell subpopulations as well as to maintain their own pool through self-renewal.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
